By Mazin Gilbert
Gen AI in Telecom: Practical Uses and Challenges
Earlier this year, I spoke at the ONE Summit, a leading industry event hosted by the Linux Foundation Networking (LFN). This summit brings together network decision-makers to discuss best practices, technical hurdles, and business opportunities within the telecom industry, from access networks to edge computing and cloud technologies. Our goal was to capture the current state of gen AI adoption within telecom companies. We shared success stories from customers and partners, analyzed challenges, and learned from past setbacks. Here’s a summary of the key takeaways, highlighting practical gen AI applications in telecom that go beyond large language models (LLMs).
Practical Use Cases of gen AI in Telecom
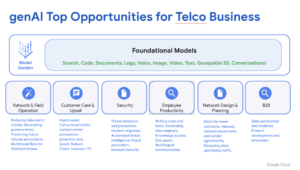
Several real-world implementations of gen AI are already making a difference:
- Instant Troubleshooting for Field Technicians: One operator integrated all their fiber rollout manuals and specifications into a gen AI system. This allows field technicians working on the fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network to troubleshoot problems in seconds – a vast improvement over the previous process, which could take minutes or even hours.
- Automated RFP Analysis: Another company automated the analysis of RFP responses using gen AI. By feeding documents into the system, they streamlined this previously time-consuming task. While success required multiple iterations, it highlighted the importance of persistence and learning from initial failures.
- Optimized ORAN Deployment: The discussion also touched on the deployment of Open Radio Access Networks (ORAN), where automation is crucial, especially for smaller operators with limited resources. AI played a key role in determining which sites or markets to prioritize for optimal network performance.
Challenges in Deploying gen AI
Several challenges to gen AI adoption emerged:
- Legal and Regulatory Uncertainty: A recurring concern was the lack of clarity surrounding the legal risks of deploying gen AI. Issues like open-source license compliance remain unresolved, and the industry is still developing a consensus on legal and regulatory frameworks. A shared understanding of these risks is crucial for wider adoption.
- Technological Limitations: Gen AI technology is still evolving. While AI is already used for tasks like predicting network congestion based on time series data, using gen AI for real-time analytics (like continuous network logs) is still under development. Although gen AI excels at processing documents and providing quick insights, real-time anomaly detection requires further advancement.
- Cost and Data Security: High development costs, legal concerns, and data ownership issues pose significant challenges. For operators exploring gen AI in cloud edge environments, data privacy and compliance are paramount. Some are considering air-gapped clouds with gen AI capabilities to ensure on-premise data security.
The Debate on Telecom-Specific LLMs
Some telecom operators are exploring the development of specialized LLMs for the industry. While many hyperscalers and startups are building their own LLMs, creating a dedicated telecom LLM is expensive due to the hardware and expertise required for training and inference. More practical approaches include:
- Prompt Tuning: Starting with basic prompt tuning for existing, general-purpose LLMs. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): Adding a retrieval stage in front of the LLM (based on search technology) to improve the accuracy of document processing.
- Fine-Tuning: Fine-tuning models on a smaller set of parameters to adapt them to telecom-specific data, which is faster and less resource-intensive than building a model from scratch.
Building a telecom-specific LLM from the ground up is seen as a last resort due to the high costs and extensive data requirements. Instead, some operators are retraining existing LLMs on telecom data, although this process is slow and resource-intensive. Hyperscalers like Google offer universal LLMs, such as the Gemini series, which can be adapted for telecom applications.
Legal and Data Security Concerns
The telecom industry must address significant legal, privacy, and data security concerns before making large-scale gen AI investments. Solutions that offer high performance, minimal errors (“hallucinations”), and ease of implementation will be crucial for rapid adoption.
Ultimately, telecom operators are responsible for the solutions they implement and the success of their gen AI deployments. A thorough understanding of the development process and expected outcomes is vital for managing daily operations and overcoming future challenges. The industry must work together to navigate these challenges and ensure the successful deployment and utilization of gen AI.
Learn more about what our customers are doing in our AI-driven Telecom video series here.